| Back to search results » | Back to search page » |
|
BALDWIN SPENCER BUILDING (OLD ZOOLOGY)
LocationTHE UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE, 156 - 292 GRATTAN STREET PARKVILLE, MELBOURNE CITY
File NumberFOL/16/6774 [PERMITS FILE ONLY]LevelRegistered |
|
Statement of Significance
What is significant?
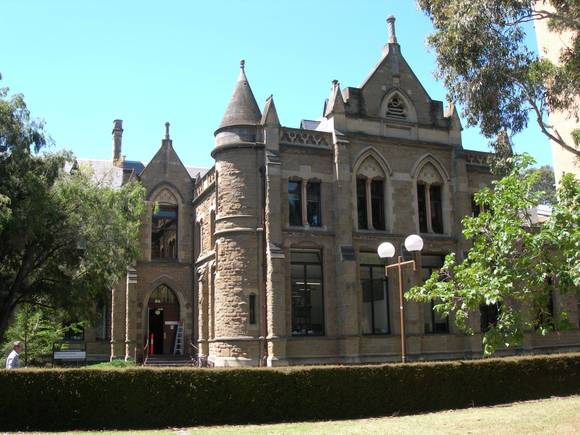
The Baldwin Spencer Building is styled in a version of the Early
English Gothic, constructed in stone and brick. The main elements are
the heavily rusticated freestone walls, buttresses, a conical roofed
round turret with spiral stair, dressed stone arched window heads,
drip moulds and a parapet decorated with trefoils. Internally the
original theatre, laboratory and staircases survive. One laboratory
retains the original slate benches. The ceiling of the library is of
panelled timber with chamfered beams and decorated circular cast iron
vents.
How is it significant?
Why is it significant?
The Baldwin Spencer Building is architecturally significant as a
masterful exposition in the Gothic style by Reed Henderson and Smart,
and compares with the old Pathology building designed by them two
years earlier. The Gothic styling is evidence of the university?s
nineteenth century preference for a consistent collegiate Gothic
styling to all its buildings. The design reflects the requirements
identified by Walter Baldwin Spencer for natural light and ventilation
in a biology research department involved in microscopic and
dissecting work. The architectural importance of the building is
enhanced by the high level of integrity of the interior spaces,
particularly the laboratories, staircases and lecture room.
The Baldwin Spencer Building was opened in 1888 as the Biology
Building. The final plans of architects Reed Henderson & Smart
faithfully followed designs submitted by the first Professor of
Biology Walter Baldwin Spencer. The new building contained a lecture
theatre to seat two hundred students, well-lit laboratories, a museum
for teaching purposes and store rooms. At the rear Spencer also
established a greenhouse, maceration room, pond, and animal compounds.
The laboratories were adapted from a design at Owens College
laboratories in England and provided for two feet of window space for
every five feet of bench space. The lecture theatre had a large
skylight roof and efficient acoustic and ventilation systems.
Additional rooms, including lecture spaces, were added in 1889. Two
workshops were added in 1905. All additions were also designed by
architects Reed Henderson and Smart, or by Smart, Tappin and Peebles
as they became by 1906. Baldwin Spencer contributed greatly to
Aboriginal research and the Darwinian debate in Australia during his
tenure at the Biology department and was instrumental in the
establishment of Wilson?s Promontory National Park in 1898. The School
of Biology was renamed Zoology in 1920 when W E Agar succeeded Baldwin
Spencer.
The Baldwin Spencer Building is of architectural and historical
significance to the State of Victoria.
The Baldwin Spencer Building is historically significant for
demonstrating the new era of science teaching and original research
that revolutionised educational policy in Victoria during the late
nineteenth century. The building demonstrates the pressure on the
University to create new science degree courses in the period
following the publication of Darwin?s The Origin of the Species. The
building is closely associated with the work of Professor Walter
Baldwin Spencer, whose expeditions into central and northern Australia
and writings on the Australian Aborigine gained world renown.
Group
Education
Category
University