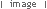| Back to search results » | Back to search page » |
|
CENTRAL PARK CONSERVATORY
Location83-141 BURKE ROAD MALVERN EAST, STONNINGTON CITY
File Number600946LevelRegistered |
|
Statement of Significance
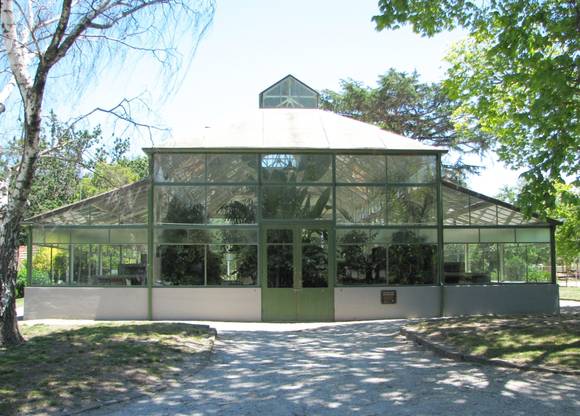
What is significant? The Central Park Conservatory was constructed in 1927. It measures 10 metres in length by 7 metres in width. It is divided into three distinct areas, the central being used for tropical plants, with display shelves located on either side with feature tiered shelving. The conservatory was constructed of wire-reinforced clear glass in a structural steel frame on a concrete base. How is it significant? The Central Park Conservatory is of historical, scientific and aesthetic significance to the State of Victoria. Why is it significant? The Central Park Conservatory is of historical significance as one of the oldest and largest extant public conservatories in Victoria. Only two other public conservatories comparable to that at Central Park exist in the State: the Rosalind Park conservatory at Bendigo, constructed in 1897, (extensive alterations were undertaken in 1978); and the conservatory in the Fitzroy gardens, which was constructed in 1930. Several other public conservatories have been demolished, making the Central Park Conservatory a now rare example of this kind of structure. The Central Park Conservatory is of scientific significance as evidence of the growth in interest in exotic plants, and the public display of plants, in the inter-war years. Its large size, tiered shelves, and expansive clear glass walls emphasise the display purposes of the conservatory, perhaps reflecting a growing knowledge of horticultural matters on behalf of a populace that was well endowed with public parks and gardens. This interest in exotic plants would not have been possible without the provision of the adjacent boiler house, integral to the functioning of conservatories at that time. The Central Park Conservatory is of aesthetic significance because of its contribution to the landscape values of one of Melbourne’s best Edwardian parks, Malvern’s Central Park. The conservatory remains in its original form, still on its initial central axis. It provides a focal point within the park, as well as providing a demarcation, visually and geographically, between the active and passive areas of the park.
Group
Parks, Gardens and Trees
Category
Conservatory