| Back to search results » | Back to search page » |
|
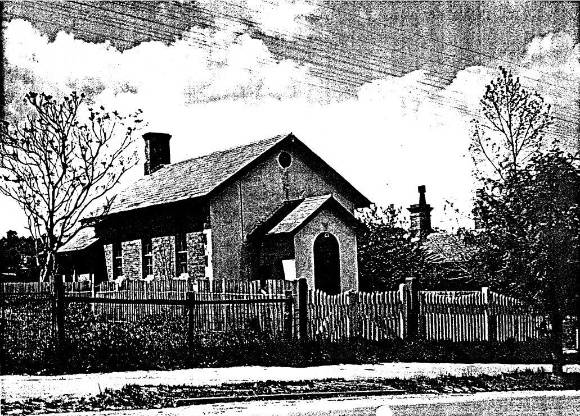
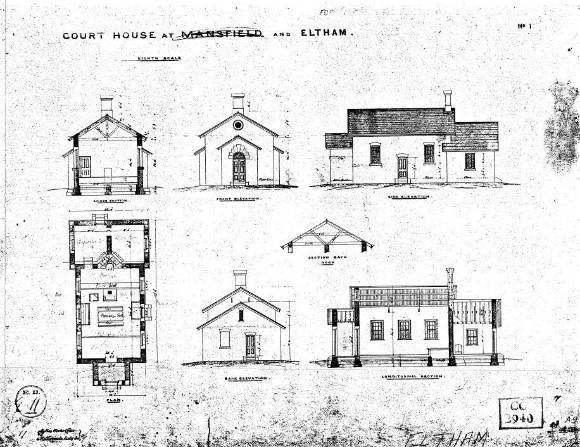
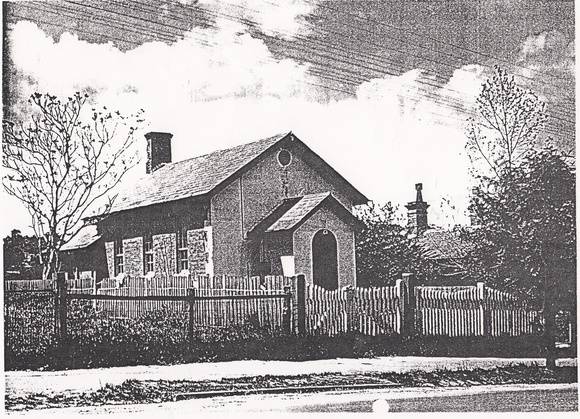
ELTHAM COURT HOUSE, former, 730 MAIN ROAD, ELTHAM
Statement of Significance
REVISED STATEMENT OF SIGNIFICANCE, CONTEXT, 2010 What is significant?
How is it significant?
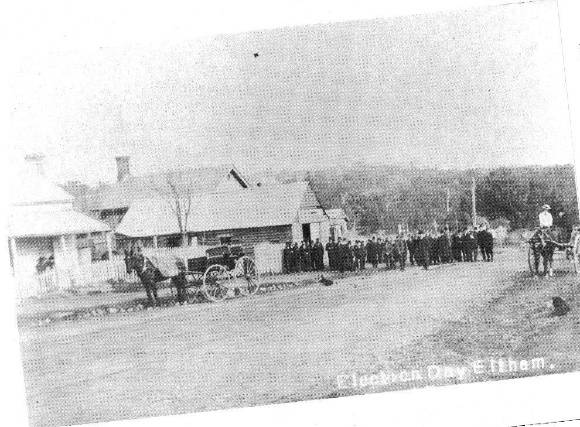
Why is it significant? BUTLER STUDY, 2001 . as one of the earliest' suburban' court houses in Greater Melbourne; . as a fine example of a mid 19th century brick rural court house ( with furnishings) from the first boom period of Colonial law and order in the immediate aftermath of a police inquiry and the effects of the gold rush - an important phase of building which sought to establish the physical presence of centralised control over law and order in the colony after the 1852 Snodgrass Committee Report on the Victorian police force and the resulting 1853 'Police Regulation Act '; . as one of two 1850s police quarters and court houses combinations to survive from this period; . as the only 19th century court house in the Nillumbik Shire; . for its important associations with the early, history of the Eltham township, its use for Eltham Road Board meetings and later school accommodation. { 2}; . as the oldest public building remaining in Eltham; and . (with the adjoining former police station)'as a major part of an important historic civic group in the Shire.
BASIS OF SIGNIFICANCE: ILLUSTRATION OF THE THEMES HISTORY ARCHITECTURE STREETSCAPE SOCIAL DEGREE OF SIGNIFICANCE:STATE SIGNIFICANCE EXTENT OF SIGNIFICANCE: ENTIRE BUILDING, FITTINGS, FURNISHINGS, MATURE EXOTIC PLANTING AND SITE
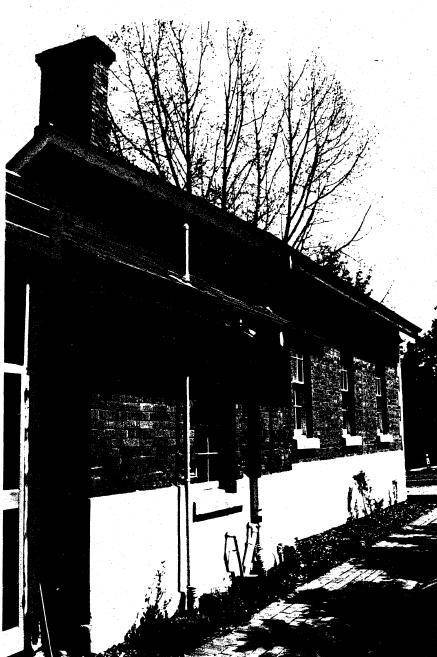
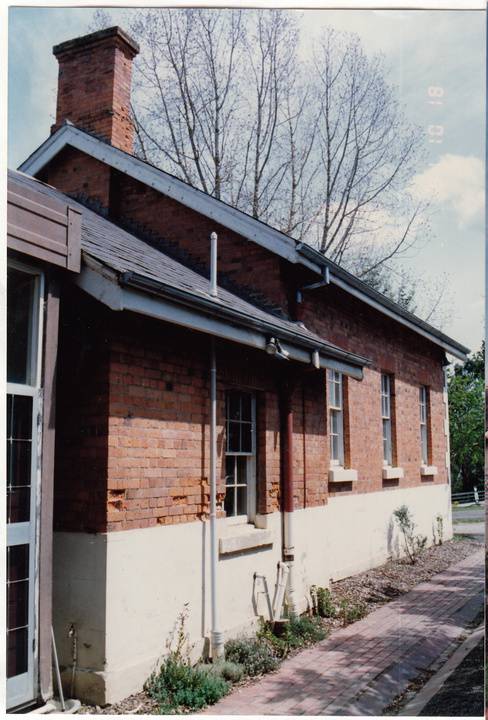
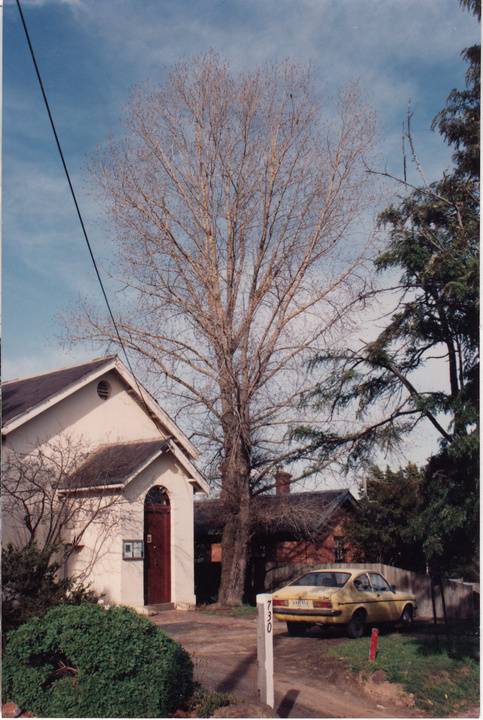
The former c1860 court house, its fittings, furnishings and the mature exotic planting and the surrounding site to the title boundaries.
The courthouse is historically and aesthetically significant to the State of Victoria.
The court house is historically significant as the oldest public building remaining in Eltham together with the former police station (HO122), as one of the earliest 'suburban' court houses in greater Melbourne and because there are only six remaining examples of similar small brick country houses (with small projecting entry porches and a gabled form) in Victoria (Criteria A & B). The court house is historically significant because its construction was intended to emphasise the centralised control over law and order in the colony in the wake of the 1852 Snodgrass committee report and the resulting Police Regulation Act (1853) (Criterion A). The court house is historically and aesthetically significant as a fine example of a mid 19th century brick rural court house constructed in the immediate aftermath of the gold rush (Criteria D & E and because, together with the former police station, it forms a major part of an important historic civic group in the Shire (Criteria A & E). The court house is aesthetically significant because it is of a modest scale and features: Italianate style eaves and exposed timber purlin ends, symmetrically placed central front porch with its round headed top-lit front door, an oculi gable end vent, twelve pane window, plinth and chimney (Criterion E).
The former Eltham Court of Petty Sessions is significant to Victoria, Nillumbik Shire and the metropolitan area:
Group
Law Enforcement
Category
Court House