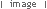| Back to search results » | Back to search page » |
|
WONTHAGGI STATE COAL MINE (EASTERN PRECINCT)
Statement of Significance
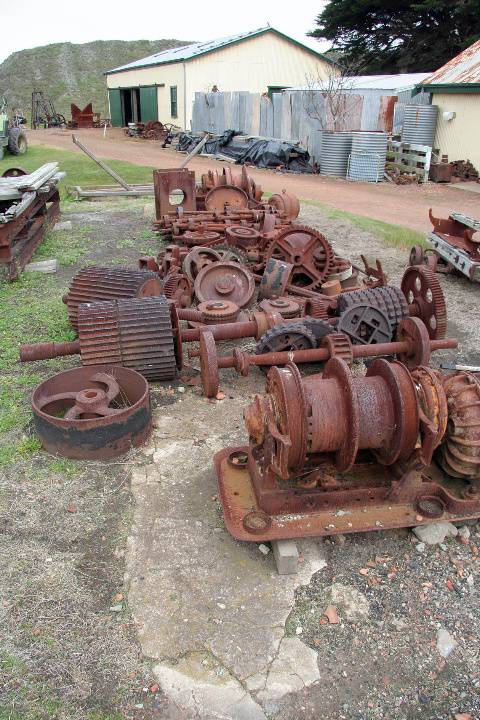
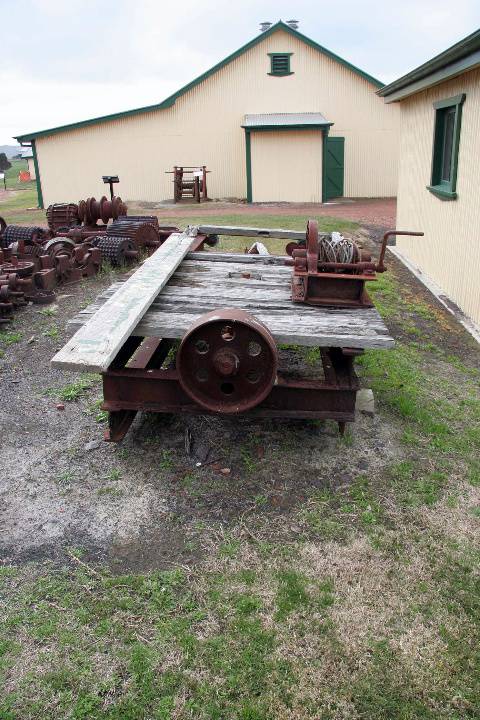
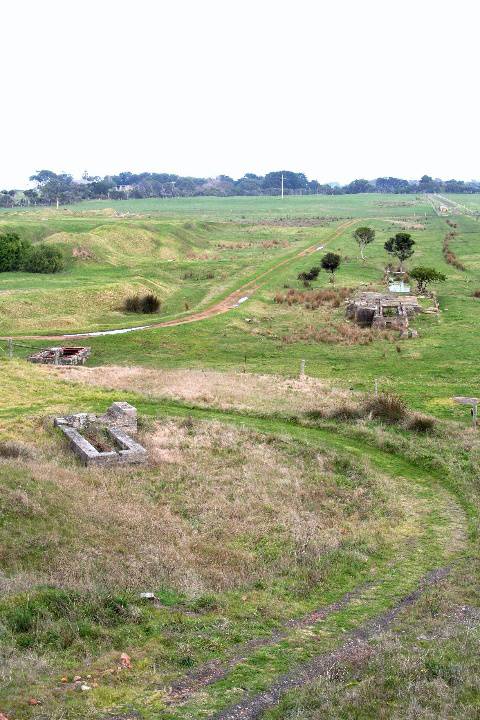
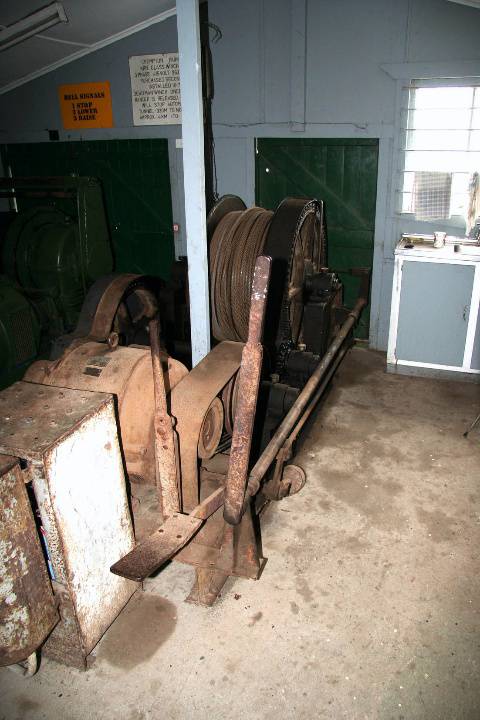
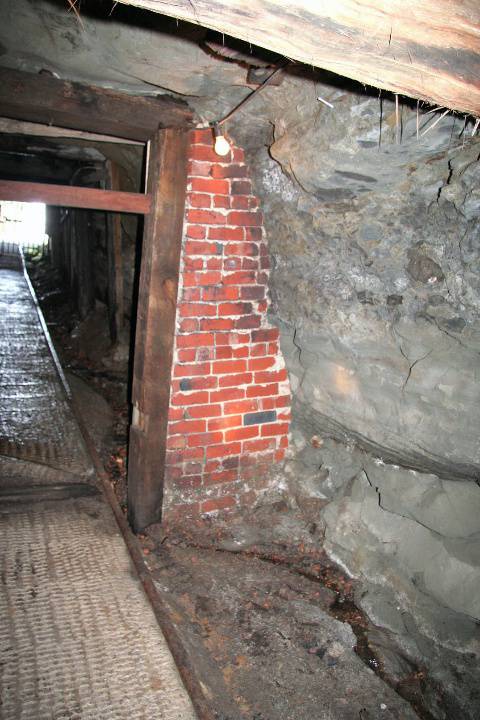
What is significant? The Wonthaggi State Coal Mine Eastern Area operated from 1919 to 1947. The Historic Reserve site includes the underground mine areas of the original No.1 bench, with three tunnels and portals, embankment and footings for winding machinery, footings for brace and electricity substation, mullock and slack heaps, railway embankment, and a number of buildings and pieces of machinery brought to the site from other parts of the State Coal Mine. At the beginning of the twentieth century black coal from New South Wales powered Victoria's railway system, gasworks and manufacturing industries. In 1909 a prolonged strike on the New South Wales coalfields threatened Victoria's economic viability, and the Victorian Government sought to end its dependence by mining its own, poorer-quality coal deposits in South Gippsland at Wonthaggi which at the time was sparsely settled and possessed no transport links with Melbourne. The first shipment of Wonthaggi coal occurred on 25 November 1909 being dispatched by bullock teams to Inverloch and thence by ship to Melbourne. Three months later transportation by rail commenced after the Railways Department constructed a line 27 miles from Nyora in the record time of ten weeks. In 1910 the Government laid out a model township and by 1921 Wonthaggi had a settled population of over 5,000 making it one of the largest towns in Gippsland. The Wonthaggi State Coal Mine, established in 1909, developed into a huge mining complex which operated until 1968. Within the first year of operation a power station was built to supply electricity to the whole area and installation was under way of the necessary engineering works for mining, ventilation, water drainage, haulage, and coal processing. At a very early stage, the mine also had a brickworks, which operated initially to construct the power station. The mine's peak period of employment was the year 1925-26 when 1,821 men were employed. During its operational life, the Wonthaggi State Coal Mine produced 16.74 million tons, making the field the largest black coal producer in the State's history and the fourth largest in Australia. At a separate mining area (in the Kirrak Basin) at the east of the township, mining on three separate bench areas occurred from 1919 to 1931, producing over 1.2 million tons. The Eastern Area site was the most south-easterly of the workings of the Kirrak basin and the more productive of the two main areas opened in the Kirrak basin. New infrastructure was required because the area was too far from existing plant. The No.1 bench at 242 metres was reached in 1916 but a down throw fault delayed reaching the No.2 bench at 731 metres. The No.3 bench at 1200 metres was reached in 1919. By 1920 the yield was 350 tons per day. A down cast shaft for ventilation was completed in 1922. Seams in the Nos. 1 and 2 benches were narrow and contained dirt bands, but the No. 3 bench seam was cleaner, 1 metre thick and more productive. Work began in 1924 to take the main heading through another fault to the 4th bench. This heading was used for haulage and the No. 18 shaft (No.18) was started in 1926 was used for ventilation and transport of ponies and men. Coal was first produced from the No.4 bench area in 1930. How is it significant? The Wonthaggi State Coal Mine Eastern Area is of historical significance to the State of Victoria Why is it significant? The Wonthaggi State Coal Mine Eastern Area is historically significant as part of the State's most significant black coal mine. The State Coal Mine reflects Victoria's endeavour to become self sufficient in the provision of vital black coal supplies to the State's railways and industry in the early twentieth century. The Eastern area including the underground workings has the potential to educate in relation to this important aspect of Victoria's history. The Wonthaggi State Coal Mine Eastern Area is significant as a representative example of a black coal mine from the first half of the twentieth century. The underground workings of the Eastern Area Historic Reserve have the potential to educate on important aspects of this industry, including the technology and working conditions of mining coal by hand and the complex organisation of labour required in such a mine.
Group
Mining and Mineral Processing
Category
Mine Shaft