| Back to search results » | Back to search page » |
|
CALOOLA (FORMER SUNBURY MENTAL HOSPITAL)
Other NamesSunbury and Macedon Ranges Special School , SUNBURY HOSPITAL FOR THE INSANE , SUNBURY LUNATIC ASYLUM , SUNBURY MENTAL HOSPITAL , SUNBURY PRIMARY SCHOOL , SUNBURY SPECIALIST SCHOOL , FORMER VICTORIA UNIVERSITY , CALOOLA CENTRE , CALOOLA TRAINING CENTRE LocationTHE AVENUE, THE HEIGHTS, HILLTOP COURT, OUTLOOK WAY, CIRCULAR DRIVE, GOLF LINKS DRIVE, BELLEVIEW DRIVE, HILLTOP COURT, SCHOOLHOUSE LANE, FLORENCE LANE, PEPPERCORN LANE, YORK PLACE AND BUCKINGHAM PLACE SUNBURY, HUME CITY
File Number602119 (1-6)LevelRegistered |
|
Statement of Significance
What is significant?
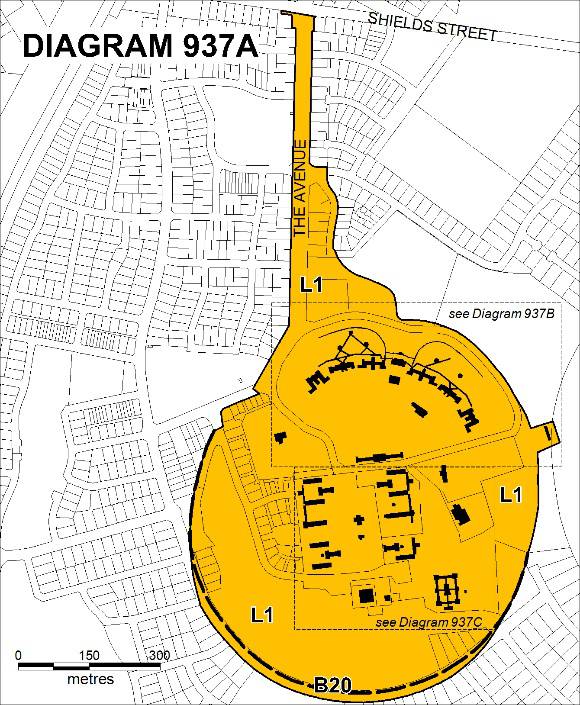
Caloola, Sunbury consists of buildings set in extensive grounds with
plantings of mature trees and remnant farmland. Caloola commenced in
1864 as an Industrial School, was redeveloped in 1879 as a Lunatic
Asylum, substantially enlarged in the period 1891 to 1914 and was
maintained in use as a psychiatric hospital (1879-1968) and later a
training centre for the intellectually disabled (1962-1992). Part of
the site became a Victoria University campus from 1994 to 2011 and the
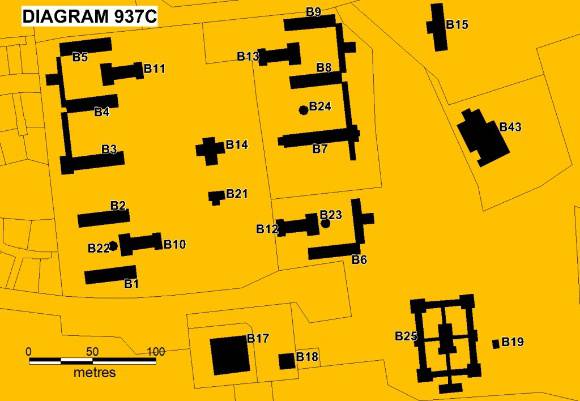
remainder is in use by the Department of Education. The Industrial School consisted of ten basalt buildings (nine
extant), designed under the direction of Public Works Department
Inspector General William Wardell and constructed in 1865-66, four
workrooms, kitchen, hospital, basalt farm building, road and stone
wall remnants which were used to house and train neglected children in
the 1860s. Boys in the Sunbury Industrial School worked on the farm
and in the tailoring and shoe-making workshops to maintain themselves
whilst in the institution and were given some basic education. Major
alterations were undertaken to the earlier basalt wards in the period
1908-12 when the buildings were linked. The Industrial School at Sunbury is believed to be the earliest
surviving example in Victoria; of the original twelve industrial
schools: only one other, constructed in 1875-76, survives at North
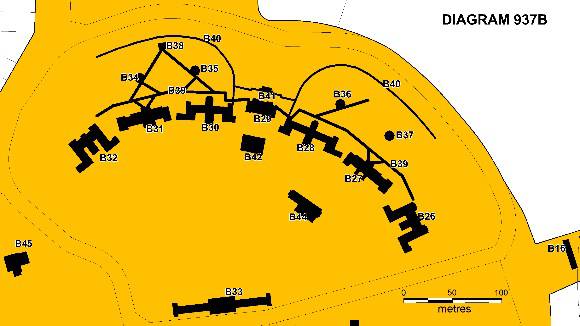
West Hospital, Parkville. The purpose built Sunbury Lunatic Asylum, constructed mainly between
1892 and 1912, was designed and constructed mainly under the direction
of the Chief Architect of the Victorian Public Works Department,
George Watson. A site plan was prepared by the talented architect
Henry Bastow in 1888. Its pavilion wards in brick with terra cotta
roofing tiles conformed to international standards of asylum and
hospital planning adopted in the later nineteenth century and were a
departure from the single monolithic buildings constructed at Kew and
Beechworth. Electric lighting was installed in the wards in 1905-6. A
tramway was laid linking the rear of the wards with the kitchen (built
1906-7) in 1908. Telephone and fire alarm systems were installed to
connect the 20 separate buildings of the asylum in 1911. The landscape designed by prominent landscape designer Hugh Linaker
dates principally from the inter-war period The landscape also
includes mature trees , mainly pines, cypress, oaks and elms and the
remains of a drystone perimeter wall and a later brick ha ha wall.
How is it significant?
Caloola is of historical, architectural, aesthetic, archaeological
and social significance to the State of Victoria.
Why is it significant?
Caloola is historically significant for the former Industrial School
buildings constructed mainly from 1865-66. The school operated from
1865 to 1879 as the first purpose-built Industrial School in Victoria.
The buildings at Sunbury are demonstrative of the harsh conditions
which characterised such schools for neglected or delinquent children.
The former Industrial School hospital (1865) is amongst the earliest
hospital buildings surviving in the state. Caloola is of historical significance for its typical asylum
landscaping and site planning, its airing courts (many of which retain
early sunshades and privies) and a complete example of a sunken wall
(or ha ha wall). Asylums were typically distant from population
centres, with extensive grounds and ha ha walls to prevent escape. Caloola is historically significant for its purpose built Sunbury
Lunatic Asylum, constructed between 1892 and 1912. Caloola's large and
architecturally impressive buildings in a curved detached pavilion
arrangement demonstrate changes in the accommodation and treatment of
mentally ill patients in the nineteenth century. The clear evidence of
farming operations also demonstrates the policy of employing boys in
industrial schools to train them in farm work and the later policy of
involving physically able mentally ill patients in outdoor work. Caloola is of historical significance for its physical fabric and
spaces which demonstrate nineteenth century attitudes to the treatment
of mental illness, including the padded cells, ripple iron cells and
dormitory accommodation. The female refractory ward, originally
designed for male criminally insane patients, demonstrates
contemporary practices in dealing with female patients who were
transferred from the general wards for disruptive behaviour. The Caloola complex is of historical significance for their
association with the talented Public Works Department architects from
the 1860s, and particularly associated with Henry Bastow and Chief
Architect George Watson, who were responsible for the design of the
pavilion buildings from the 1890s to 1912. Its association with noted
landscape designer, Hugh Linaker, who was responsible for the grounds
from 1912, is also significant. The Caloola site is of archaeological significance for its potential
to contain historical archaeological features, deposits and relics
that relate to the construction and use of the Industrial School and
the Lunatic Asylum. Caloola is of architectural significance for its institutional
buildings of the 1860s and the 1890s. Its industrial school buildings
of the 1860s are typical of the Public Works Department output of the
1860s, use local material, have simple classically derived detailing
and gain much of their importance by the repetition of forms. Major
alterations were undertaken to the earlier basalt wards in the period
1908-12 when the buildings were linked. The planning of these links is
accomplished and contributed to the continuity of use of the site and
represented changing attitudes to mental health. The site at Sunbury is architecturally significant for its rare and
intact examples of an industrial school and a late nineteenth century
lunatic asylum. The site contains rare examples of hairpin fencing
used to enclose airing courts for patients. Outdoor shelters or
sunshades for patients are also uncommon in Victoria. The Caloola complex is of architectural significance for its
industrial school and asylum buildings. The earliest of the remaining
buildings of the Sunbury Industrial School are architecturally
significant as forming the earliest purpose built example of its
type,. They are important for their bluestone construction and austere
style which distinguished them from the later asylum buildings. The
1860s buildings which exhibit classically derived detailing are
constructed of local basalt. The red brick and timber buildings of the
principal phase of asylum expansion of 1891 to 1912 are of
architectural significance for innovative design as a pavilion
hospital grouping and include distinctive detailing. Caloola is architecturally significant as a former lunatic asylum,
one of several surviving in the state. It demonstrates typical
characteristics such as formal planning, use of sunken walls (ha ha
walls), airing courts and a diverse range of building types to cater
for the patient and staff population. They gain their architectural
significance from the unity of materials, overall cohesiveness of
design, consistent and distinctive detailing (especially in the
unusual use of buttresses and steep roofs in the former hospital
wards), impressive site planning and spacious setting. The Caloola complex is of aesthetic significance for the quality and
range of its architecture and garden elements, consistent use of
basalt, red brick and terra cotta tiles, its consistency of
architectural styles and materials within the two major building
phases, for its landscape planning and plantings and for its prominent
siting on the hill with views to and from the site.
.
Caloola is of social significance especially to past patients and
their families as a reminder of past practices in mental health care. The Caloola site is on the traditional land of the Wurundjeri people.
The Caloola complex is of historical significance for its
demonstration of attitudes to child welfare and mental health in its
early industrial school buildings and asylum buildings, airing courts
and gardens. .
Group
Health Services
Category
Hospital